In today’s fast-paced world, effective communication plays a vital role in the success of any business. Whether it’s sharing information with colleagues, giving instructions to employees, or presenting ideas to clients, business communication is at the core of every interaction in a company. But what exactly does the process of business communication involve? Let’s break it down in simple terms.
What is Communication?
Communication is the exchange of information, ideas, or feelings between individuals or groups. It involves both sending and receiving messages, which can be verbal, non-verbal, written, or visual. Effective communication ensures that the intended message is understood accurately. Whether it’s a casual conversation or a formal report, communication plays a crucial role in human interaction.
What is Business Communication?
Business communication is simply the exchange of information within a business or between businesses and outside entities for the purpose of achieving business goals. Whether it’s a simple email or a formal presentation, communication is an integral part of daily operations. The business communication process goes beyond just speaking or writing; it involves understanding the audience, selecting the right medium, and delivering the message clearly and effectively.
For further clarification, It involves the interaction between employees, management, stakeholders, and customers. The objective is to ensure that everyone is aligned with the company’s vision, policies, and goals. Clear business communication leads to better collaboration, productivity, and decision-making within the organization.
Importance of Effective Communication in Business
Why does business communication matter? Imagine trying to work in a company where no one shares information or updates each other on important tasks. Projects would fail, customers would be dissatisfied, and the entire operation could fall apart. Effective communication ensures that everyone is on the same page, tasks are completed efficiently, and businesses thrive. It fosters better relationships between team members, enhances collaboration, and drives success.
Enhances Productivity
Effective business communication ensures that employees have a clear understanding of their roles, responsibilities, and tasks. When instructions and expectations are communicated clearly, it minimizes confusion and allows employees to focus on their work, resulting in higher productivity.
Builds Relationships
Strong communication fosters trust and collaboration within the organization and with external stakeholders. Open lines of communication help build rapport, improve teamwork, and encourage positive relationships, which are essential for long-term success.
Facilitates Decision-Making
Clear communication allows managers to gather accurate, relevant information, leading to more informed decisions. When everyone is on the same page, it becomes easier to assess situations and make sound business choices that benefit the company.
Prevents Misunderstandings
By conveying messages clearly and concisely, business communication reduces the risk of errors and misinterpretations. This prevents potential setbacks and ensures smoother operations, as everyone is aligned on expectations and objectives.
Boosts Employee Morale
Open communication encourages employees to express their concerns, ideas, and feedback. This creates a positive work environment where employees feel valued, leading to higher job satisfaction, increased engagement, and overall better morale.
Related: Barriers to Effective Communication
Types of Business Communication

Business communication can be categorized into four major types:
- Internal, upward communication: When employees share information with their superiors, such as progress reports or suggestions.
- Internal, downward communication: When management communicates important information, policies, or feedback to employees.
- Internal, lateral communication: This involves communication between colleagues or teams on the same hierarchical level.
- External communication: Interactions between the company and outside stakeholders like customers, suppliers, or investors.
Verbal and Non-Verbal Communication
Verbal communication refers to the use of words to convey messages, either through speaking or writing. Non-verbal communication, on the other hand, involves gestures, body language, facial expressions, and even tone of voice. While verbal communication conveys the content, non-verbal communication often reveals emotions and attitudes.
Formal and Informal Communication Channels
In a business, communication can occur through formal or informal channels:
- Formal Communication: This includes official channels such as emails, reports, presentations, and meetings. It is typically structured and follows the company’s rules and procedures.
- Informal Communication: Also known as the grapevine, informal communication happens through casual conversations or instant messaging. It’s unstructured and can flow freely within the organization.
7 Steps of the Communication Process
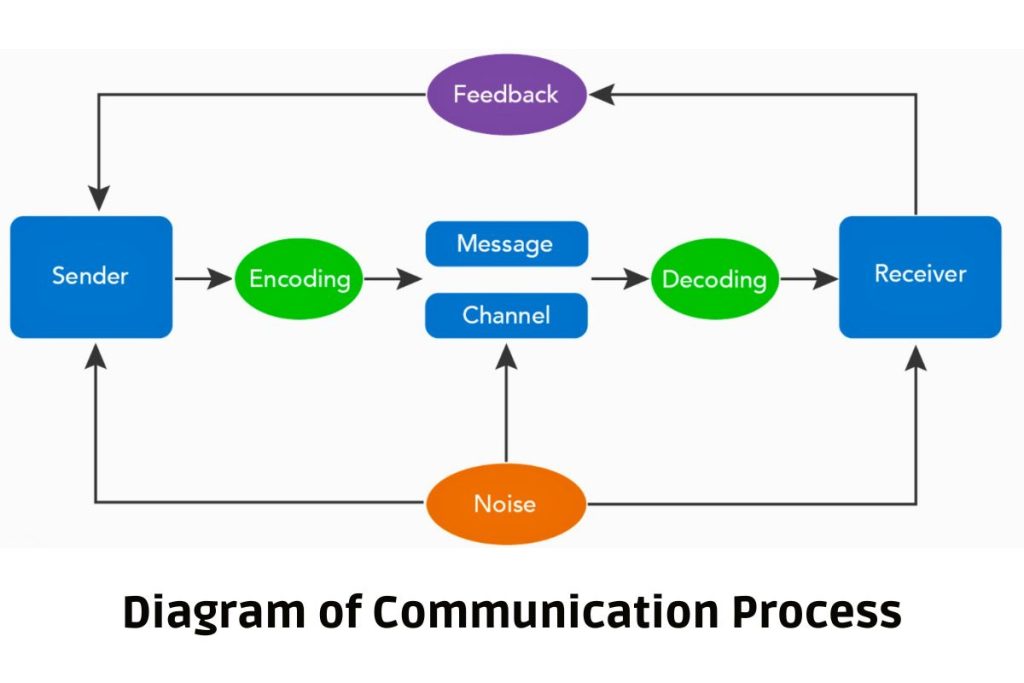
The communication process is a systematic series of steps that ensures the effective transmission of information from one party to another. Understanding these steps in detail is essential to improving communication skills, both in personal and business contexts. Let’s explore each stage of the process with examples:
1. Sender
The sender is the originator of the message. This individual has an idea, thought, or piece of information they want to convey to another party. The sender initiates the communication process by deciding to share that information.
Example: A manager wants to inform their team about an upcoming meeting. In this case, the manager is the sender.
2. Message
The message is the actual content being communicated. It can include information, thoughts, feelings, or instructions that the sender wants to share. The clarity and accuracy of the message are crucial to ensuring it is understood as intended.
Example: The message in the manager’s case is, “The team meeting will be held on Monday at 10 AM to discuss the project updates.”
3. Encoding
Encoding is the process through which the sender converts the message into a form that the receiver will understand. This involves choosing the right language, tone, and symbols that best represent the message. The sender must consider the receiver’s background, culture, and knowledge when encoding.
Example: The manager decides to encode the message in simple, direct language using email, knowing that this is the preferred communication channel for the team.
4. Channel / Medium
The channel is the medium through which the message is transmitted. Channels can be verbal (phone calls, meetings) or non-verbal (emails, texts, body language). The sender must choose an appropriate channel based on the situation and the receiver’s preferences.
Example: The manager sends the message via email because it allows the team to read it at their convenience and serves as a formal reminder.
5. Receiver
The receiver is the person or group for whom the message is intended. The receiver’s role is to comprehend the message accurately. The receiver’s ability to decode the message properly depends on their understanding of the context, language, and intent.
Example: The team members who read the email are the receivers of the message.
6. Decoding
Decoding is the process through which the receiver interprets or makes sense of the message. This involves understanding the language, symbols, and context of the message. The success of communication depends on how accurately the receiver decodes the message.
Example: One team member reads the email and decodes the message to understand that there’s a meeting scheduled on Monday at 10 AM to discuss project updates.
7. Feedback
Feedback is the receiver’s response to the sender’s message. It indicates whether the message has been understood correctly and allows the sender to clarify any confusion. Feedback can be verbal or non-verbal and helps close the communication loop.
Example: A team member replies to the email, confirming their availability for the meeting, which serves as feedback to the manager that the message has been received and understood.
8. Noise
Noise refers to any form of interference that affects the delivery, reception, or understanding of the message. Noise can be external (such as a poor internet connection) or internal (such as distractions, preconceptions, or emotional barriers). Noise can distort the message or lead to misunderstanding.
Example: If one team member is distracted while reading the email and misreads the meeting time as 11 AM instead of 10 AM, this is an example of internal noise affecting the decoding process.
Conclusion
The communication process involves a sequence of steps that ensures the successful exchange of information. For communication to be effective, both the sender and the receiver must actively engage in the process, with attention to potential barriers like noise. By understanding this process, individuals can improve how they convey and interpret messages, resulting in clearer and more productive interactions.
More Articles:

